Types of Motor Starters and Motor Starting Techniques
What is a Motor Starter?
A motor starter is an electrical device that is used to start & stop a motor safely. Similar to a relay, the motor starter switches the power ON/OFF & unlike a relay, it also provides a low voltage & overcurrent protection.
The main function of a motor starter is;
- To safely start a motor
- To safely stop a motor
- To reverse the direction of a motor
- To protect the motor from low voltage & overcurrent.
A motor starter is made of two main components that work together to control & protect the motor;
- Electrical Contactor: The purpose of the contactor is to switch ON/OFF the power supply to the motor by making or breaking the contact terminals.
- Overload protection circuit: The purpose of this circuit is to protect the motor from potential harm due to the overload condition. Huge current through the rotor may damage the winding as well as other appliances connected to the supply. It senses the current & breaks the power supply.
Why We Need a Starter with a Motor?
A motor starter is essential for starting an induction motor. It is because of its low rotor impedance. The rotor impedance depends on the slip of the induction motor which is the relative speed between the rotor & stator. The impedance varies inversely with the slip.
The slip of the induction motor is at maximum i.e. 1 at standstill (rest position), thus the impedance is at its minimum & it draws a huge amount of current called inrush current. The high inrush current magnetizes the air gap between the rotor & stator that induces an EMF in the rotor winding. This EMF produces an electrical current in rotor winding that creates a magnetic field to generate torque in the rotor. As the rotor speed increases the slip of the motor decreases & the current drawn by the motor is reduced.
The high inrush current is 5-8 times the normal rated full load current. So such amount of current can damage or burn the windings of the motor that will render the machine useless & it can cause a huge dip in voltage of the supply line that can damage other appliances connected to the same line.
In order to protect the motor from such a huge amount of currents, we use a starter that limits the initial current for a short duration at startup & once the motor attains a certain speed, the normal power supply to the motor is resumed. They also provide protection against fault conditions such as low voltage & overcurrent during normal operation.
Although small motors rated below 1 horsepower have high impedance and they can withstand the initial current thus they do not need such motor starter, however, they do need overcurrent protection system which is provided by the DOL (Direct On-Line) starters. The above explanation shows that why we need a starter to install with a motor?
How a Motor Starter Works?
A starter is a control device that is used for switching the motor either manually or automatically. It is used for safe ON/OFF control of electrical motors by making or breaking its contacts.
The manual starter is used for smaller motors where the hand operated lever is manually operated (move the contacts position) to the ON or OFF position. The disadvantage of these kinds of starters is that they need to switch ON after power frailer. In other words, they need manual control for each (ON or OFF) operation. Sometimes, this operation may leads to flow high currents in the motor winding which may burn the motor. This is why it is not recommended in most cases where other alternative motor starters with protection are used such as automatic starters.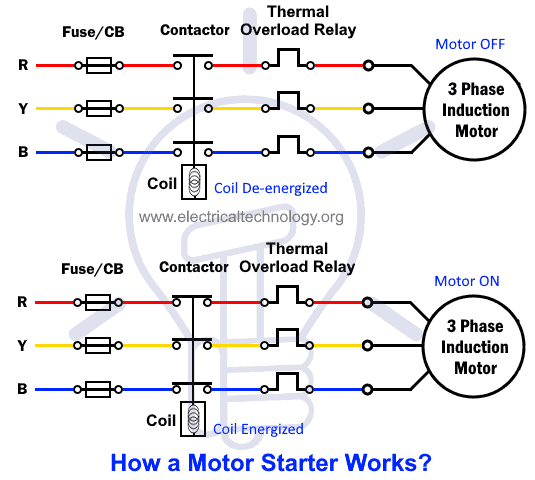
On the other hand, the automatic starters which consist of electromechanical relays and contactors are used to switch the motor ON/OFF operation. When current passes through the contactor coils, it energizes and produces the electromagnetic field which pulls or pushes the contacts to make the connection of motor windings to the power supply.
The start and stop push buttons connected to the motor and starter can be used for ON and OFF operation of motors. The contactor coils can be de-energize by pushing the stop button which leads to de-energize the coil. This way, the contactor contacts move back due to spring arrangement to its normal position which leads to switch off the motor. In case of power failure or manual switch-off operation, the motor won’t start automatically until we manually start the motor by pressing the “start push button”. The following diagram shows that how a DOL motor starter operates for ON/OFF operation.
Types of Motor Starters Based on Starting Methods & Techniques
In industries, various starting techniques are used to start an induction motor. Before discussing the types of motors, here are some of the techniques used in motor starters.
-
Full Voltage or Across The Line Starter
Such starters directly connect the motor with the power line providing the full voltage. The motors connected through such starters have low power ratings so that they do not create a huge voltage drop in the power line. They are used in an application where motors have low ratings & need to run in one direction.
-
Full Voltage Reversing Starter
3 phase induction motor’s direction can be reversed by swapping any two phases. Such a starter incorporates two mechanically interlocked magnetic contactors with swapped phases for forward & reverse direction. It is used in an application where the motor needs to run in both directions & the contactors are used to control it.
-
Multispeed Starter
In order to vary the speed of an AC motor, you need to vary the AC supply frequency or vary the number of poles (by reconnecting the windings in some) of the motor. Such types of starter run the motor in a few pre-selected speeds to meet its applications.
-
Reduced Voltage Starter
The most common type of starting technique is to reduce the voltage at the starting of the motor to reduce the inrush current that could damage the windings of the motor & also cause a huge dip in voltage. These starters are used for high rated motors.
Based on the techniques described above, the following types of motor starters are used in industries.
Type of Motor Starters:
We will discuss the following types of motors and their starting methods based on the above motor starting methods with advantages and disadvantages.
- Direct Online Starter (DOL)
- Stator Resistance starter
- Rotor Resistance or Slip Ring Motor Starter
- Autotransformer Starter
- Star Delta Starter
- Soft Starter
- Variable frequency drive (VFD)
The motor starters have many types but mainly they are classified into two types.
-
Manual Starter
This type of starter operates manually and does not require any experience. A push-button is used to turn OFF & ON the motor connected with it. The mechanism behind the button includes a mechanical switch that breaks or makes the circuit to stop or start the motor.
They also provide overload protection. However, these starters do not have LVP (low voltage protection) i.e. it does not break the circuit upon power failure. It can be dangerous for some applications because the motor restarts when the power is restored. Thus they are used for a low power motor. Direct On-Line (DOL) starter is a manual starter that provides overload protection.
-
Magnetic Starter
Magnetic starters are the most common type of starter & they are mostly used for high power AC motors. These starters operate electromagnetically like a relay that breaks or makes the contacts using magnetism.
It provides a lower & safer voltage for starting & also includes protection against low voltage & overcurrent. During the power failure, the magnetic starter automatically breaks the circuit. Unlike manual starters, it includes automatic & remote operation that excludes the operator.
The magnetic starter consists of two circuits;
- Power circuit; this circuit is responsible for supplying power to the motor. It consists of electrical contacts that turn ON/OFF the power supplied from the supply line to the motor through overload relay.
- Control circuit; this circuit controls the contacts of the power circuit to either make or break the power supply to the motor. The electromagnetic coil energizes or de-energizes to pull or push the electrical contacts. Thus providing a remote control for the magnetic starter.
Direct Online (DOL) Starter
DOL aka Direct Online Starter is the simplest form of motor starter that connects the motor directly to the power supply. It consists of a magnetic contactor that connects the motor with a supply line & an overload relay for protection against overcurrent. There is no voltage reduction for safe starting a motor. Therefore the motor used with such starters has below 5 hp rating. It has two simple push buttons that start & stop the motor.
Pressing the start button energizes the coil that pulls the contactors together to close the circuit. And pressing the stop button de-energizes the contactor’s coil & pushes its contacts apart thus breaking the circuit. The switch used for turning ON/OFF the power supply can be of any type such as rotary, level, float, etc.
Although, this starter does not provide safe starting voltage the overload relay provides protection against overheating & overcurrent. The overload relay has normally closed contacts that energize the contactor’s coil. When the relay trips, the contactor’s coil de-energize and break the circuit.
Advantages of DOL Motor Starter
- it has a very simple & cost-effective design.
- It is very easy to understand & operate.
- it provides high starting torque due to the high starting current.
Disadvantages of DOL Motor Starter
- The high inrush current can damage the windings
- The high inrush current causes voltage dip in the power line.
- It is not suitable for heavy motors
- It can decrease the lifespan of a motor
Stator Resistance starter
Stator resistance starter uses the RVS (reduced voltage starter) technique to start a motor. External resistance is added in series with each phase of a 3 phase induction motor’s stator. The resistor’s job is to reduce the line voltage (subsequently reducing the initial current) applied to the stator.
Initially, the variable resistor is kept at maximum position offering maximum resistance. Therefore the voltage across the motor is minimum (in safe level) due to the voltage drop across the resistor. The low stator voltage limits the starting inrush current that can damage the motor windings. As the motor picks up the speed, the resistance is reduced & the stator phase is directly connected to the power lines.
As the current is directly proportional to the voltage & torque varies to the square of the current, a 2 times decrease in the voltage decreases the torque by 4 times. Thus the starting torque using such a starter is very low & needs to be maintained.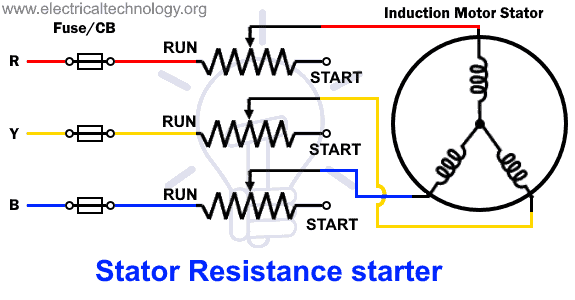
Advantages of stator resistance motor starter
- It provides flexibility in starting characteristics.
- The variable voltage supply allows smooth acceleration
- It can be connected to both star or delta connected motor.
Disadvantages of stator resistance motor starter
- The resistors dissipate the power
- The starting torque is very low due to voltage reduction
- The resistors are quite expensive for large motors.
Rotor Resistance or Slip Ring Motor Starter
This type of motor starter works on a full voltage motor starting technique. It works only on a slip ring induction motor that is why it is also known as a slip ring motor starter.
External resistances are connected with the rotor in star combination through the slip ring. These resistors limit the rotor current & increase the torque. This, in turn, reduces the starting stator current. It also helps in improving the power factor
The resistors are only used during the starting of the motor & it is removed once the motor picks up its rated speed.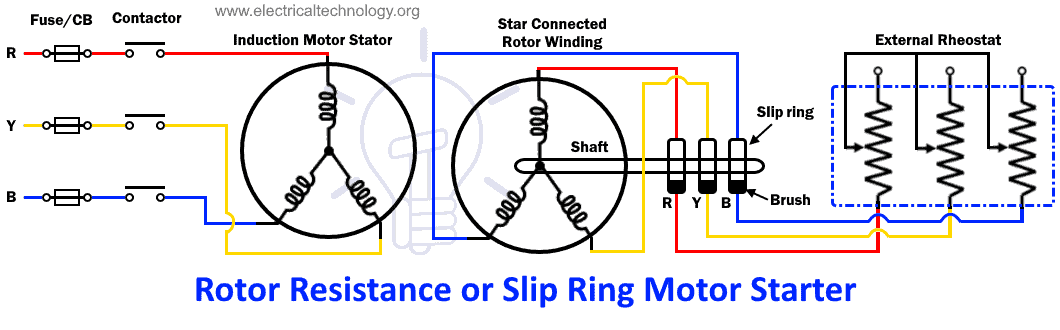
Advantages of Rotor Resistance Motor Starter
- It provides a low starting current using full voltage.
- Due to high starting torque, the motor can be started under load
- This method improves the power factor.
- It provides a wide range of speed control
Disadvantages of Rotor Resistance Motor Starter
- It only works on slip ring induction motor
- The rotor is expensive & heavier.
Autotransformer Starter
Such type of motor starters uses an autotransformer as a step-down transformer to reduce the voltage applied to the stator during the starting stage. It can be connected to both star & delta connected motors.
The autotransformer’s secondary is connected with each phase of the motor. The multiple tapings of autotransformer provide a fraction of the rated voltage. During starting, the relay is at the start position i.e. the tap point providing a reduced voltage for the startup. The relay switches between the tap points to increase the voltage with the speed of the motor. At last, it connects it with the full rated voltage.
As compared to other voltage reduction techniques, it offers high voltage for a specific starting current. It helps in providing a better starting torque.
Advantages of Autotransformer Starter
- It provides a better starting torque.
- It is used for starting large motors with a significant load.
- It also offers manual speed control.
- It also offers flexibility in starting characteristics.
Disadvantages of Autotransformer Starter
- Due to large size of the autotransformer, such a starter takes too much space.
- The circuit is complex & relatively expensive than other starters.
Star Delta Starter
This is another common starting method used in industries for large motors. The windings of 3 phase induction motor are switched between star and delta connection to start the motor.
To start the induction motor, it is connected in star using a triple pole double throw relay. The phase voltage in star connection is reduced by the factor 1/√3 & it reduces the starting current as well as the starting torque by 1/3 of the normal rated value.
When the motor accelerates, a timer relay switches the star connection of the stator windings into the delta connection, allowing the full voltage across each winding. The motor runs at rated speed.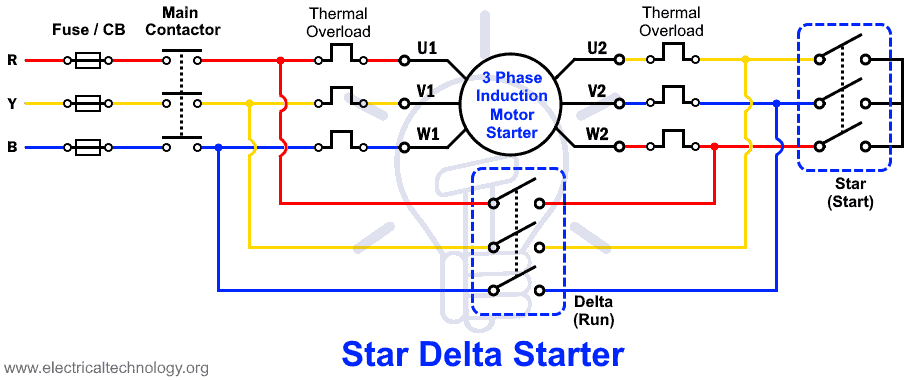
Advantages of Star Delta Starter
- Its design is simple & cheap
- It does not require maintenance
- Provide a low surge current.
- It is used for starting large induction motors.
- It is best for long acceleration time.
Disadvantages of Star Delta Starter
- It works on delta connected motor
- There are more wire connections.
- It offers low starting torque which cannot be maintained.
- There is very limited flexibility is starting characteristics.
- There is a mechanical jerk while switching from star to delta.
Soft Starter
The soft starter also uses the voltage reduction technique. It uses the semiconductor switches like TRIAC to control the voltage as well as the starting current supplied to the induction motor.
A phase-controlled TRIAC is used to provide variable voltage. The voltage is varied by varying the conduction angle or firing angle of the TRIAC. The conduction angle is kept at minimum to provide reduced voltage. The voltage is increased gradually by increasing the conduction angle. At maximum conduction angle, the full line voltage is applied to the induction motor & it runs at rated speed.
It provides a gradual & smooth increase in the starting voltage, current as well as the torque. Thus there is no mechanical jerk & provide a smooth operation that increases the life span of the machine.
Advantages of Soft Starter
- It provides better control over starting current & voltage
- It offers smooth acceleration, thus no jerks.
- It reduces the power surges in the system.
- Extends the life span of the system
- Provide better efficiency & lack the need for maintenance
- Its size is small
Disadvantages of Soft Starter
- It is relatively expensive
- There is energy dissipation in the form of heat
Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)
Just like the soft starter, a Variable frequency drive (VFD) can vary the voltage as well as the frequency of the supplying current. It is mainly used for controlling the speed of the induction motor as it depends on the supply frequency.
The AC from the supply line is converted into DC using rectifiers. The pure DC is converted into AC with adjustable frequency & voltage using pulse width modulation technique through power transistor like IGBTs.
It provides full control over the motor speed from 0 to rated speed. The speed adjust option with the variable voltage provides a better starting current & acceleration.
Advantages of Variable Frequency Drive
- It provides a better and smooth acceleration for large motor
- It offers full speed control with smooth acceleration & deceleration.
- It increases the life span due to the absence of electrical & mechanical stress
- It offers forward & reverse operation of a motor
Disadvantages of Variable Frequency Drive
- It is relatively expensive unless speed control is necessary
- There is heat dissipation
- VFDs create harmonics in the electric lines which can affect electronic equipment & power factor.
Related Posts:
- Star-Delta (Y-Δ) 3-phase Motor Starting Method by Automatic star-delta starter with Timer.
- Three Phase Motor Connection STAR/DELTA Without Timer – Power & Control Diagrams
- Three Phase Motor Connection Star/Delta (Y-Δ) Reverse / Forward with – Timer Power & Control Diagram
- Starting & Stopping of 3-Phase Motor from more than One Place Power & Control diagrams
- Three Phase Slip Ring Rotor Starter Control & Power Diagrams
- Even More Three Phase Motor Power & Control Wiring Diagrams
- Speed Control of DC Motor – Voltage, Rheostatic & Flux Control Methods
- Single-Phase Induction Motor – Construction, Working, Types & Applications
- DC Machine – Construction, Working, Types and Applications
- Speed Control of DC Motor – Voltage, Rheostatic & Flux Control Methods

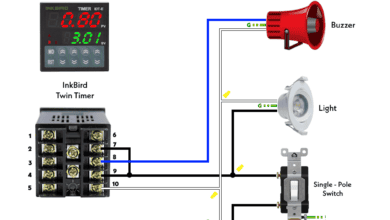 How to Wire Twin Timer for Repeated ON-Delay in Cycle Mode?
How to Wire Twin Timer for Repeated ON-Delay in Cycle Mode? Wire Twin Timer in Repeat Cycle & One-Shot Mode for 120V/240V Motors?
Wire Twin Timer in Repeat Cycle & One-Shot Mode for 120V/240V Motors?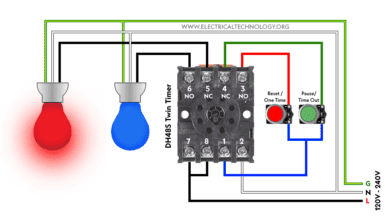 How to Wire Twin Timer for 120V/240V Circuits – ON/OFF Delay
How to Wire Twin Timer for 120V/240V Circuits – ON/OFF Delay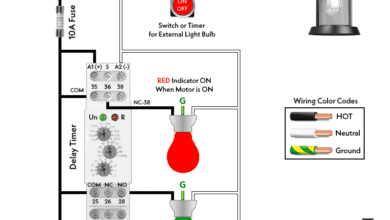 How to Wire Multifunction ON/OFF Delay Timer for 120V/240V Motors?
How to Wire Multifunction ON/OFF Delay Timer for 120V/240V Motors? How to Wire One-Shot Timer using Twin Timer For Delay?
How to Wire One-Shot Timer using Twin Timer For Delay? How to Control 120V & 240V Water Heater using ST01 Timer and Contactors?
How to Control 120V & 240V Water Heater using ST01 Timer and Contactors?